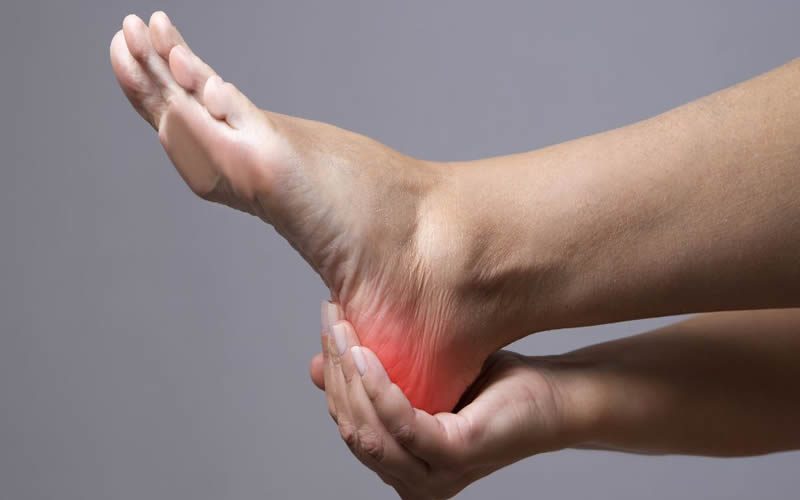
Do you find yourself wincing with every step, hindered by persistent foot pain? The complexities of nerve-related foot discomfort can often leave you bewildered. From burning sensations to tingling discomfort, nerve problems in the feet can take various forms. You’re in the right place if you’re seeking clarity on these nerve-related foot pains and their impact.
Understanding Nerve-Related Foot Pain
Foot pain is a common concern arising from various causes, including nerve-related issues. When nerves in the feet are affected, they can send signals of discomfort, pain, tingling, numbness, or weakness. These sensations can vary in intensity and location, making it important to understand the intricacies of nerve-related foot pain to ensure accurate diagnosis and effective treatment.
1. Nerves and Their Role
Nerves are vital in transmitting signals between the brain and the rest of the body. In the context of the feet, nerves are responsible for relaying sensory information, such as touch, temperature, and pain. Nerves also help control the muscles, enabling movement and balance. However, when nerves become damaged, compressed, or irritated, they can send aberrant signals, resulting in uncomfortable sensations.
2. Causes of Nerve Problems
Nerve-related foot pain can stem from various causes, including:
- Injury: Trauma or repetitive stress can lead to nerve damage. Sprains, fractures, or overuse injuries can cause inflammation around nerves, resulting in pain signals.
- Compression: Nerves can become compressed when pinched or squeezed by surrounding structures. This can occur due to tight footwear, anatomical abnormalities, or swelling.
- Medical Conditions: Underlying medical conditions such as diabetes, autoimmune disorders, and vascular diseases can contribute to nerve damage and foot pain.
- Nerve Diseases: Conditions like neuropathy, specifically targeting nerves, can lead to widespread foot discomfort.
3. Types of Nerve-Related Foot Pain
Nerve-related foot pain can manifest in various ways:
- Sharp Pain: Nerve compression or inflammation can cause sharp, shooting pains that may radiate along the nerve’s pathway.
- Burning Sensation: Some individuals experience a burning or tingling sensation in their feet, often indicating nerve irritation.
- Numbness: Nerve damage can decrease sensation or numbness in specific foot areas.
- Weakness: Nerves play a role in muscle control. When nerves are affected, weakness in the associated muscles may occur.
4. Localisation of Pain
Nerve-related foot pain can be localised or radiate to other areas. The pain may be limited to a specific point where the nerve is affected or spread to other parts of the foot, leg, or lower back. Understanding the pattern and location of the pain can help podiatrists pinpoint the underlying cause.
5. Importance of Accurate Diagnosis
Accurately diagnosing the source of nerve-related foot pain is essential for effective treatment. Medical practitioners may employ a combination of physical examinations, medical history reviews, and diagnostic tests such as nerve conduction studies, X-rays, or MRI scans. Identifying the root cause of the pain is crucial in tailoring a treatment plan that addresses the underlying issue, providing relief and improving the individual’s overall quality of life.
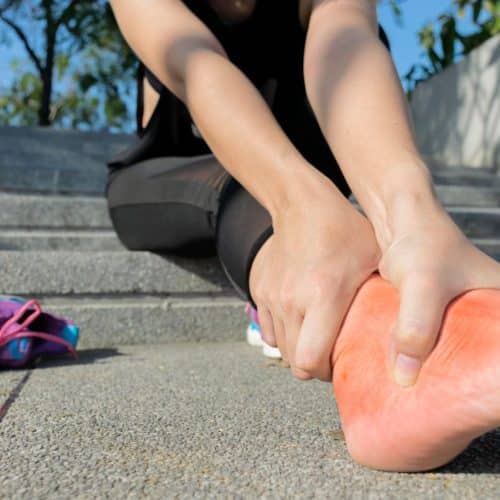
Plantar Fasciitis: A Nerve-Based Discomfort
Plantar fasciitis is a common and often painful condition that affects the feet, causing discomfort and hindering mobility. While not exclusively a nerve problem, the condition can lead to nerve-related sensations due to its impact on the plantar fascia—a thick band of tissue that runs along the sole. Understanding the intricacies of plantar fasciitis, its causes, symptoms, and treatment options can help individuals manage this condition effectively.
1. Causes and Symptoms
Plantar fasciitis occurs when the plantar fascia, a tissue band connecting the heel bone to the toes, becomes inflamed. This inflammation can stem from various factors, including:
- Overuse: Repetitive stress on the feet, often due to excessive walking, running, or standing, can strain the plantar fascia and lead to inflammation.
- Foot Mechanics: People with flat feet, high arches, or abnormal walking patterns may be more prone to developing plantar fasciitis due to uneven weight and pressure distribution.
- Age and Weight: Age and excess body weight can contribute to the development of plantar fasciitis, as the plantar fascia loses elasticity over time and added weight places extra stress on the feet.
Common symptoms of plantar fasciitis include:
- Heel Pain: The hallmark symptom is a sharp, stabbing pain in the heel, especially noticeable during the first steps in the morning or after rest periods.
- Pain After Activity: Pain may also intensify after prolonged standing, walking, or physical activity periods.
- Stiffness: Individuals with plantar fasciitis often experience stiffness and discomfort in the affected foot, particularly after periods of inactivity.
2. Treatment Options
Managing plantar fasciitis involves a combination of self-care strategies and medical interventions. Here are some common approaches:
- Rest and Ice: Resting the affected foot and applying ice can help reduce inflammation and alleviate pain in the acute phase. Massage and heat are then recommended to assist healing.
- Stretching: Gentle calf and foot stretches can help improve flexibility and relieve tension on the plantar fascia.
- Footwear: Wearing supportive shoes with proper arch support and cushioning can reduce strain on the plantar fascia.
- Orthotic Inserts: Custom orthotic inserts can provide additional support and help correct foot mechanics.
- Medications: Over-the-counter nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) may help manage pain and inflammation intially.
- Physical Therapy: A physical therapist can guide individuals through targeted exercises to strengthen foot muscles and improve flexibility.
- Night Splints: Wearing night splints can help keep the foot in a dorsiflexed position, stretching the plantar fascia during sleep.
- Corticosteroid Injections: In cases of severe pain, corticosteroid injections may provide temporary relief.
- Shockwave Therapy: This non-invasive procedure stimulates healing and reduces pain in the affected area.
- Surgery: Surgical intervention is rarely needed but may be considered if conservative treatments fail to provide relief after an extended period.
It’s important to note that the effectiveness of treatments can vary from person to person. Consulting a healthcare practitioner, such as a podiatrist or orthopedic specialist, is crucial for an accurate diagnosis and personalised treatment plan. With proper care and management, individuals with plantar fasciitis can relieve pain, improve their foot health, and regain mobility.
Plantar fasciitis, although not solely a nerve-related issue, can lead to nerve-based discomfort due to its impact on the plantar fascia. By understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatment options for plantar fasciitis, individuals can take proactive steps to manage their foot pain and improve their overall quality of life.
Morton’s Neuroma: Nerve Pain Between Toes
Morton’s neuroma is a specific type of nerve-related foot pain that often affects the area between the third and fourth toes. This condition involves the thickening of tissue around a nerve leading to the toes, typically the plantar digital nerve. Morton’s neuroma can result in discomfort and pain, making it essential to understand its causes, symptoms, and available treatment approaches.
1. Causes and Symptoms
Morton’s neuroma is commonly caused by the compression and irritation of the plantar digital nerve as it passes between the metatarsal bones in the foot. Several factors can contribute to the development of this condition:
- Footwear: Wearing tight, narrow shoes or high heels can squeeze the toes together, increasing pressure on the nerves.
- Foot Structure: People with certain foot deformities, such as high arches or flat feet, may be more prone to developing Morton’s neuroma.
- Activities: Engaging in activities involving repetitive pressure on the forefoot, such as running or sports, can contribute to developing this condition.
Common symptoms of Morton’s neuroma include:
- Pain: Individuals with Morton’s neuroma often experience sharp, shooting pain or a burning sensation between the toes, typically the third and fourth toes.
- Tingling: Some people may feel tingling or numbness in the affected area.
- Feeling of an Object: Some describe the sensation of having a pebble or fold in their sock, even when there is nothing there.
- Pain Relief: The discomfort may temporarily improve by removing shoes, massaging the area, or avoiding activities that exacerbate the pain.
2. Treatment Approach
Managing Morton’s neuroma involves a combination of conservative treatments to relieve symptoms and address the underlying causes. Here are some approaches that healthcare practitioners might recommend:
- Footwear Modification: Wearing shoes with a wider toe box and lower heels can reduce pressure on the affected nerve.
- Orthotic Inserts: Custom orthotic inserts can help correct foot mechanics and alleviate pressure on the nerve.
- Padding: Metatarsal pads or cushions can help redistribute pressure away from the affected nerve.
- Icing: Applying ice to the painful area can help reduce inflammation and provide temporary relief.
- Medications: Over-the-counter pain relievers or anti-inflammatory drugs may help manage pain and discomfort.
- Physical Therapy: Stretching and strengthening exercises can improve foot mechanics and alleviate pressure on the nerve.
- Injection Therapy: Corticosteroid injections may reduce inflammation and provide short-term pain relief.
- Surgical Options: In cases where conservative treatments fail to provide relief, surgical neuroma removal may be considered.
Consulting a healthcare practitioner for an accurate diagnosis and personalised treatment plan is important. Early intervention is key to preventing the progression of Morton’s neuroma and achieving effective pain management.
Morton’s neuroma is a nerve-based foot condition that can cause significant discomfort between the toes. Understanding its causes, recognising the symptoms, and exploring various treatment options can help individuals manage the pain associated with this condition.
Tarsal Tunnel Syndrome: Nerve Compression Woes
Tarsal tunnel syndrome is characterised by the compression or entrapment of the tibial nerve as it passes through a narrow space called the tarsal tunnel—a channel located along the inside of the ankle and below the bony prominence on the inside of the ankle. This syndrome can lead to various nerve-related discomforts in the foot and ankle area. Understanding the causes, signs, and potential treatments for tarsal tunnel syndrome is essential for effective management and relief.
1. Causes and Signs
Tarsal tunnel syndrome often arises due to pressure on the tibial nerve caused by various factors, including:
- Ankle Sprains or Injuries: Trauma to the ankle, such as a sprain or fracture, can lead to swelling and compression of the tibial nerve.
- Flat Feet: Individuals with flat feet or fallen arches are more prone to tarsal tunnel syndrome due to the altered mechanics of the foot.
- Enlarged Structures: Swelling, inflammation, or growth within the tarsal tunnel can impinge on the tibial nerve.
Common signs and symptoms of tarsal tunnel syndrome include:
- Pain: Individuals often experience shooting or burning pain along the inside of the ankle, which can radiate to the sole.
- Tingling and Numbness: Tingling or numbness can be felt in the bottom of the foot or toes.
- Muscle Weakness: Weakness in the foot muscles can lead to difficulties in walking and maintaining balance.
2. Treatment Possibilities
Managing tarsal tunnel syndrome involves addressing the underlying causes and relieving the pressure on the tibial nerve. Here are some potential treatment approaches:
- Rest and Elevation: Resting and elevating the affected foot can help reduce swelling and alleviate pressure on the nerve.
- Orthotic Inserts: Custom orthotic inserts can provide proper arch support and help alleviate pressure on the tibial nerve.
- Medications: Over-the-counter pain relievers and anti-inflammatory drugs can help manage pain and reduce inflammation.
- Physical Therapy: Specific exercises and stretches can improve foot mechanics, strengthen supportive muscles, and alleviate nerve compression.
- Foot mobilisation therapy: to increase movement within the joint and decompress the nerve.
- Surgical Intervention: In severe cases where conservative treatments fail to provide relief, surgical decompression of the tibial nerve may be considered.
3. Preventive Measures
Preventing tarsal tunnel syndrome involves adopting healthy habits and practices:
- Proper Footwear: Wearing shoes that provide adequate support and cushioning can help prevent excess pressure on the tibial nerve.
- Stretching: Regularly stretching the calf muscles and maintaining good foot flexibility can reduce the risk of nerve compression.
- Weight Management: Maintaining a healthy weight can lessen the stress on the feet and lower the chances of nerve-related issues.
Tibial nerve compression in the ankle area characterises tarsal tunnel syndrome. Recognising the causes, signs, and available treatment options is essential for effectively managing this condition.
By addressing contributing factors, following recommended treatments, and adopting preventive measures, individuals can find relief from the discomfort associated with tarsal tunnel syndrome and enhance their overall foot health.
Diabetic Neuropathy: Nerve Problems in Diabetes
Diabetic neuropathy is a complex and often challenging complication of diabetes that involves nerve damage caused by high blood sugar levels. This condition can affect various body parts, including the feet, leading to significant discomfort and potential complications. Understanding the impact of diabetic neuropathy on the feet, its symptoms, and effective management strategies is crucial for individuals living with diabetes.
1. Impact on Feet
Diabetic neuropathy can profoundly affect the nerves that serve the feet. Prolonged exposure to high blood sugar levels can damage the nerve fibres that transmit sensory information and control muscle function. As a result, individuals with diabetic neuropathy may experience:
- Loss of Sensation: Nerve damage can lead to decreased or complete loss of sensation in the feet. This loss of feeling makes it difficult to detect injuries, cuts, or blisters.
- Tingling and Burning: Some individuals may experience tingling, burning, or prickling sensations in the feet, which can be uncomfortable and affect daily activities.
- Muscle Weakness: Nerve damage can result in muscle weakness, leading to difficulties in walking, balance, and coordination.
- Foot Deformities: The loss of sensation and muscle function can contribute to the development of foot deformities, such as hammertoes or Charcot’s foot.
2. Managing Diabetic Foot Pain
Effectively managing diabetic neuropathy and its impact on the feet is essential for preventing complications. Here are some strategies individuals can consider:
- Blood Sugar Control: Maintaining tight control over blood sugar levels through proper diabetes management can help prevent or slow the progression of neuropathy.
- Foot Care: Regularly inspecting the feet for cuts, blisters, or sores and keeping them clean and moisturised can reduce the risk of infections.
- Proper Footwear: Wearing shoes that fit well and provide ample support can prevent pressure points and reduce the risk of foot injuries.
- Nerve-Protecting Creams: Topical creams containing certain vitamins or medications may help protect and soothe damaged nerves.
- Pain Management: Medications specifically designed to manage neuropathic pain can relieve discomfort.
3. Seeking Professional Guidance
Individuals with diabetes should work closely with their healthcare team to effectively manage diabetic neuropathy. Regular check-ups with a podiatrist or endocrinologist are crucial for monitoring foot health and addressing any emerging issues promptly.
Sciatica and Foot Pain: The Nerve Connection
Sciatica is a term that describes a set of symptoms rather than a specific condition. It refers to the irritation or compression of the sciatic nerve, the longest nerve in the body, running from the lower back down to the feet. Sciatica can lead to a variety of discomforts, including foot pain. Understanding the role of the sciatic nerve, its impact on foot health, and effective strategies for addressing sciatica-induced foot pain is essential for those experiencing these symptoms.
1. The Sciatic Nerve’s Role
The sciatic nerve originates from the lower spinal cord and branches through the lower back, hips, buttocks, and each leg. It is a major signal transmission pathway between the brain and the lower body. When the sciatic nerve becomes compressed or irritated—often due to conditions affecting the spine—it can lead to sciatica symptoms.
2. Addressing Sciatica-Induced Foot Pain
Sciatica can manifest as foot pain, making it important to identify and address the underlying cause. Here are some steps to consider:
- Consult a Healthcare Practitioner: If you experience persistent foot pain, especially if it radiates from the lower back or buttocks, consulting a healthcare practitioner is crucial. They can diagnose the underlying cause of the pain and recommend appropriate treatment.
- Identify the Source: Sciatica-induced foot pain is typically caused by issues in the lower back, such as herniated discs, spinal stenosis, or nerve root compression. Imaging tests like MRI or CT scans can help pinpoint the source of the problem.
- Physical Therapy: A physical therapist can develop a personalised exercise program to strengthen muscles, improve posture, and alleviate pressure on the sciatic nerve.
- Pain Management: Over-the-counter pain relievers, anti-inflammatory drugs, or muscle relaxants can help manage pain and discomfort.
- Stretching and Yoga: Gentle stretches that target the lower back and legs and yoga poses that promote flexibility and relaxation can relieve sciatic pain.
- Epidural Steroid Injections: In more severe cases, a healthcare practitioner may recommend corticosteroid injections to reduce inflammation and provide relief.
- Surgical Intervention: Surgery may be considered if conservative treatments fail to alleviate symptoms and the underlying issue requires surgical correction.
3. Preventive Measures
Even while not all cases of sciatica may be avoided, there are several behaviours that, when practised regularly, can lessen the likelihood of an individual having the condition:
- Maintain Good Posture: Proper posture while sitting, standing, and lifting can help protect the spine and reduce the risk of nerve compression.
- Stay Active: Regular exercise focusing on core strength, flexibility, and cardiovascular health can support overall spine health.
- Lift Correctly: Using proper lifting techniques to avoid straining the lower back when lifting heavy objects.
Sciatica-induced foot pain can be a challenging and discomforting experience. By understanding the role of the sciatic nerve, identifying the underlying causes, and exploring various treatment options, individuals can take proactive steps to address their symptoms.
Whether through conservative approaches, pain management, or medical interventions, finding effective strategies to alleviate sciatica-induced foot pain can improve overall well-being and enhance foot health.
Lifestyle Adjustments for Nerve Pain Management
Making targeted lifestyle adjustments can be crucial in effectively managing nerve-related foot pain. By incorporating habits and practices prioritising foot health and overall well-being, individuals can alleviate discomfort and enhance their quality of life. Here are some lifestyle adjustments to consider:
- Mindful Movement: Engage in low-impact exercises that promote circulation and strengthen muscles without putting excessive strain on the feet, such as swimming, cycling, or tai chi.
- Proper Footwear: Choose shoes that provide adequate arch support, cushioning, and a comfortable fit. Avoid high heels and tight shoes that can exacerbate nerve pain.
- Foot-Friendly Activities: Opt for activities that minimise the impact on the feet, such as gentle yoga, water aerobics, or stationary biking.
- Balanced Diet: Consume a nutrient-rich diet that includes foods high in vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants. These nutrients support nerve health and overall well-being.
- Stay Hydrated: Drinking enough water maintains optimal circulation, supports nerve function, and prevents dehydration-related issues.
- Stress Reduction: Engage in stress-relief techniques like meditation, deep breathing, or mindfulness to lower stress levels, which can contribute to nerve pain.
- Appropriate Weight Management: Maintaining a healthy weight reduces pressure on the feet, minimising the risk of nerve compression.
- Ergonomic Workspace: If your work involves prolonged sitting, ensure your workspace is ergonomically designed to support proper posture and reduce strain on the lower back and feet.
- Regular Stretching: Incorporate stretching routines targeting the feet, legs, and lower back. Stretching can alleviate tension and promote flexibility.
- Supportive Footwear at Home: Opt for supportive footwear, even at home, to provide constant comfort and support to your feet.
- Foot Elevation: Elevate your feet whenever possible to reduce swelling and improve blood circulation.
- Adequate Sleep: Prioritise quality sleep to support the body’s healing and regeneration processes.
- Consultation with Specialists: Regularly visit healthcare practitioners, such as podiatrists, physical therapists, or orthopedic specialists, for expert guidance on managing nerve pain.
- Mindful Walking: Pay attention to your gait and stride while walking. Ensure your steps are even and avoid overstriding to reduce the impact on the feet.
- Avoid Smoking: Smoking can negatively impact circulation and exacerbate nerve-related issues. Quitting smoking can lead to improved overall foot health.
- Limit Alcohol: Excessive alcohol consumption can contribute to inflammation and hinder the body’s healing processes. Moderation is key.
- Stay Active: Maintain an active lifestyle within your comfort level, as regular movement supports circulation and prevents muscle stiffness.
- Stay Informed: Continuously educate yourself about proper foot care, nerve health, and new techniques for managing nerve-related pain.
By incorporating these lifestyle adjustments into your daily routine, you can effectively manage nerve-related foot pain and work towards improved comfort, mobility, and overall well-being. Always consult healthcare practitioners to tailor these adjustments to your needs and circumstances.
Conclusion
In conclusion, understanding the various types of foot pain caused by nerve problems is crucial for maintaining optimal foot health. From tingling sensations to shooting pain, nerve-related foot problems can significantly impact one’s quality of life. By identifying the specific type of foot pain and its underlying nerve issue, individuals can seek appropriate medical attention and take proactive steps to alleviate discomfort.
It’s important to remember that foot pain should not be ignored or brushed aside. If you or someone you know is experiencing persistent foot pain, it’s advisable to consult a podiatrist for accurate diagnosis and guidance. Nerve problems can manifest in different ways, and seeking timely medical attention can prevent the pain from worsening and affecting daily activities.
Now that you’ve learned about the various types of foot pain caused by nerve problems, have you ever experienced any of these symptoms? Whether it’s a tingling sensation, numbness, or shooting pain in your feet, understanding the potential causes can empower you to take control of your foot health.
Feel free to share your thoughts or experiences in the comments below – let’s start a conversation about foot pain and nerve-related issues!
Content Summary
- The complexities of nerve-related foot discomfort can often leave you bewildered.
- From burning sensations to tingling discomfort, nerve problems in the feet can take various forms.
- Understanding these nuances is essential to finding effective solutions and relief for those suffering from these nerve problems.
- Discover how these issues affect your daily life, potential treatment options, and expert advice to help you navigate this intricate landscape of foot pain and nerve problems.
- Foot pain is a common concern arising from various causes, including nerve-related issues.
- When nerves in the feet are affected, they can send signals of discomfort, pain, tingling, numbness, or weakness.
- These sensations can vary in intensity and location, making it important to understand the intricacies of nerve-related foot pain to ensure accurate diagnosis and effective treatment.
- Nerve-related foot pain can be localised or radiate to other areas.
- Understanding the pattern and location of the pain can help podiatrists pinpoint the underlying cause.
- Accurately diagnosing the source of nerve-related foot pain is essential for effective treatment.
- Identifying the root cause of the pain is crucial in tailoring a treatment plan that addresses the underlying issue, providing relief and improving the individual’s overall quality of life.
- Understanding the intricacies of plantar fasciitis, its causes, symptoms, and treatment options can help individuals manage this condition effectively.
- Individuals with plantar fasciitis often experience stiffness and discomfort in the affected foot, particularly after periods of inactivity.
- Managing plantar fasciitis involves a combination of self-care strategies and medical interventions.
- Consulting a healthcare practitioner, such as a podiatrist or orthopedic specialist, is crucial for an accurate diagnosis and personalised treatment plan.
- With proper care and management, individuals with plantar fasciitis can relieve pain, improve their foot health, and regain mobility.
- Morton’s neuroma is commonly caused by the compression and irritation of the plantar digital nerve as it passes between the metatarsal bones in the foot.
- Wearing tight, narrow shoes or high heels can squeeze the toes together, increasing pressure on the nerves.
- Individuals with Morton’s neuroma often experience sharp, shooting pain or a burning sensation between the toes, typically the third and fourth toes.
- Managing Morton’s neuroma involves a combination of conservative treatments to relieve symptoms and address the underlying causes.
- Over-the-counter pain relievers or anti-inflammatory drugs may help manage pain and discomfort.
- Tarsal tunnel syndrome is characterised by the compression or entrapment of the tibial nerve as it passes through a narrow space called the tarsal tunnel—a channel located along the inside of the ankle and below the bony prominence on the inside of the ankle.
- This syndrome can lead to various nerve-related discomforts in the foot and ankle area.
- Understanding the causes, signs, and potential treatments for tarsal tunnel syndrome is essential for effective management and relief.
- Trauma to the ankle, such as a sprain or fracture, can lead to swelling and compression of the tibial nerve.
- Individuals often experience shooting or burning pain along the inside of the ankle, which can radiate to the sole.
- Managing tarsal tunnel syndrome involves addressing the underlying causes and relieving the pressure on the tibial nerve.
- Resting and elevating the affected foot can help reduce swelling and alleviate pressure on the nerve.
- Maintaining a healthy weight can lessen the stress on the feet and lower the chances of nerve-related issues.
- Tibial nerve compression in the ankle area characterises tarsal tunnel syndrome.
- Recognising the causes, signs, and available treatment options is essential for effectively managing this condition.
- By addressing contributing factors, following recommended treatments, and adopting preventive measures, individuals can find relief from the discomfort associated with tarsal tunnel syndrome and enhance their overall foot health.
- Diabetic neuropathy is a complex and often challenging complication of diabetes that involves nerve damage caused by high blood sugar levels.
- This condition can affect various body parts, including the feet, leading to significant discomfort and potential complications.
- Understanding the impact of diabetic neuropathy on the feet, its symptoms, and effective management strategies is crucial for individuals living with diabetes.
- Effectively managing diabetic neuropathy and its impact on the feet is essential for preventing complications.
- Individuals with diabetes should work closely with their healthcare team to effectively manage diabetic neuropathy.
- Regular check-ups with a podiatrist or endocrinologist are crucial for monitoring foot health and addressing any emerging issues promptly.
- Understanding the role of the sciatic nerve, its impact on foot health, and effective strategies for addressing sciatica-induced foot pain is essential for those experiencing these symptoms.
- Addressing Sciatica-Induced Foot Pain
- Sciatica can manifest as foot pain, making it important to identify and address the underlying cause.
- Consulting a podiatrist is crucial if you experience persistent foot pain, especially if it radiates from the lower back or buttocks.
- They can diagnose the underlying cause of the pain and recommend appropriate treatment.
- Proper posture while sitting, standing, and lifting can help protect the spine and reduce the risk of nerve compression.
- Sciatica-induced foot pain can be a challenging and discomforting experience.
- By understanding the role of the sciatic nerve, identifying the underlying causes, and exploring various treatment options, individuals can take proactive steps to address their symptoms.
- Whether through conservative approaches, pain management, or medical interventions, finding effective strategies to alleviate sciatica-induced foot pain can improve overall well-being and enhance foot health.
- Making targeted lifestyle adjustments can be crucial in effectively managing nerve-related foot pain.
- Engage in low-impact exercises that promote circulation and strengthen muscles without putting excessive strain on the feet, such as swimming, cycling, or tai chi.
- In conclusion, understanding the various types of foot pain caused by nerve problems is crucial for maintaining optimal foot health.
- By identifying the specific type of foot pain and its underlying nerve issue, individuals can seek appropriate medical attention and take proactive steps to alleviate discomfort.
- If you or someone you know is experiencing persistent foot pain, it’s advisable to consult a podiatrist for accurate diagnosis and guidance.
FAQs
1. Can nerve-related foot pain be prevented?
Maintaining a healthy weight, using suitable footwear, and engaging in regular exercise might lower the chance of developing plantar fasciitis. However, it is only possible to avoid some instances.
2. How can I differentiate between regular foot pain and nerve-related foot pain?
Nerve-related foot pain often includes sensations like tingling, numbness, or burning that extend beyond the foot’s surface.
3. Are there non-surgical treatment options for nerve-related foot pain?
Yes, many cases of nerve-related foot pain can be managed with conservative approaches, including physical therapy, medication, and lifestyle adjustments.
4. Is diabetic neuropathy reversible?
While it may not be completely reversible, proper management of diabetes and neuropathy can significantly improve symptoms and prevent further progression.
5. When should I seek medical attention for foot pain?
If foot pain is severe, persistent, or interfering with your daily activities, it’s advisable to consult a podiatrist for an accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment.