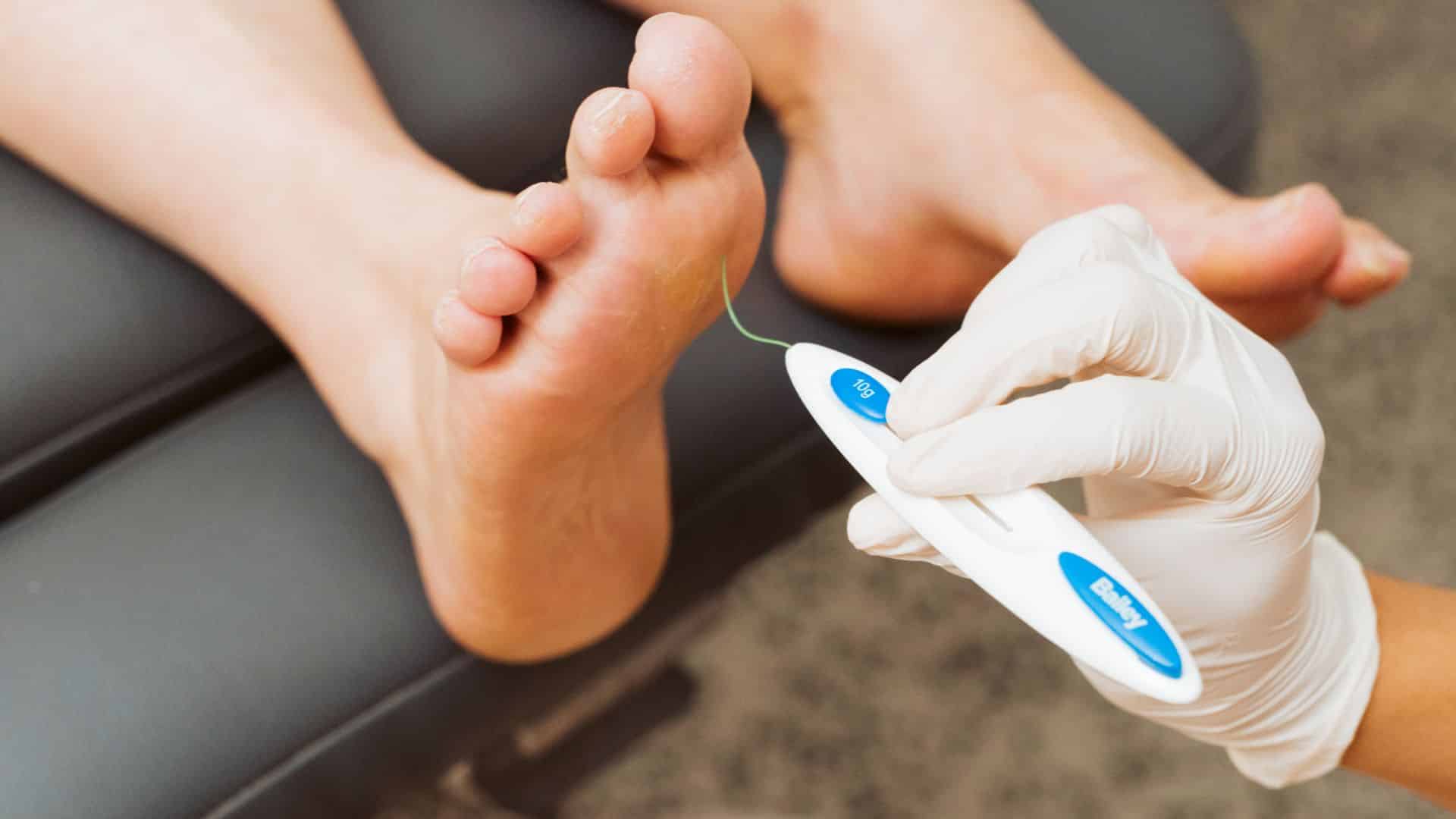
Peripheral neuropathy occurs when there is damage to the nerves to the peripheries (hands, toe etc). This results in the loss of feeling and temperature sensation to the effected area.
The reason for numbness in the feet in people with diabetes is still largely unknown. It is believed to be associated with high blood sugar levels and unstable diabetes affecting the nerve sheath fibers and message impulses. The longer you have had diabetes the greater risk of peripheral neuropathy.
Risk Factors of Peripheral Neuropathy (Numbness in the Feet):
-
Foot ulcerations and burns – due to being unable to detect trauma/injury to feet.
-
Infections– if unaware trauma has occurs and wound left untreated.
-
Increased risk of falls – due to changes in leg muscles, proprioception and foot structure, altering the walking style.