Hello, and thank you for visiting our guide on a topic that concerns millions of people all around the world. No matter if you are an athlete, a fitness fanatic, or just someone who loves remaining active, it is crucial to have a solid awareness of the underlying issues that cause knee discomfort, as well as the variety of treatment options that are most likely to be successful.
What is Knee Pain?
Knee pain is a frequent problem that may affect people of any age and be brought on by a wide range of various types of activity. Whether you are an athlete, a fitness enthusiast, or someone who follows a more sedentary lifestyle, experiencing soreness in the knees may significantly impact your quality of life.
In order to attain effective management and long-term relief from knee pain, it is essential to get a grasp of the factors that contribute to the condition and the treatment choices currently accessible. In this article, we will investigate the multiple factors that may lead to knee discomfort, and we will also investigate the several therapy methods that might assist you in regaining mobility and comfort.
Common Causes of Knee Pain
1. Osteoarthritis
Osteoarthritis is a chronic degenerative joint disease that gradually wears down the protective cartilage that cushions the ends of bones in a joint. As the cartilage deteriorates, the bones can rub against each other, causing pain, stiffness, and reduced range of motion. While osteoarthritis can affect any joint, it commonly targets the knees due to the significant weight-bearing and movement they endure. Factors such as aging, genetics, obesity, joint injuries, and repetitive stress contribute to osteoarthritis in the knees.
2. Injuries
- Ligament Tears: Ligament tears, especially the anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) and medial collateral ligament (MCL) are prevalent among athletes and those involved in activities that involve sudden stops, changes in direction, or direct blows to the knee. These tears often cause immediate pain, swelling, and instability.
- Meniscus Tears: The meniscus is a C-shaped piece of cartilage that acts as a shock absorber between the thighbone and shinbone. Tears in the meniscus can result from twisting movements or direct trauma, leading to pain, swelling, and limited knee movement.
- Fractures: Fractures of the bones around the knee can occur due to accidents, falls, or high-impact injuries. Fractures are accompanied by severe pain, swelling, bruising, and an inability to bear weight on the affected leg.
3. Tendinitis
Tendinitis refers to inflammation of a tendon, which connects muscle to bone. Patellar tendinitis, commonly known as “jumper’s knee,” involves the inflammation of the patellar tendon that connects the kneecap (patella) to the shinbone (tibia). This condition often affects individuals who engage in activities that require frequent jumping or explosive leg movements, leading to pain just below the kneecap.
4. Bursitis
Bursae are relatively tiny sacs that are filled with fluid and act as a cushioning mechanism between bones, tendons, and muscles. Bursitis is a condition that can occur if the bursae become irritated and inflamed as a consequence of repeated movements, extended kneeling, or direct damage. Bursitis of the knee is characterised by localised pain, swelling, and tenderness in the vicinity of the afflicted bursa.
5. Overuse
Engaging in repetitive movements, especially without adequate rest and recovery, can strain the knee joint and its surrounding structures. Activities such as running, cycling, or kneeling can lead to overuse injuries, causing pain, inflammation, and discomfort in the knee area.
6. Obesity
Carrying excess body weight increases knee joint stress, accelerating wear and tear. The excessive load can contribute to the breakdown of cartilage, leading to conditions like osteoarthritis. Managing body weight through a balanced diet and regular exercise can help alleviate stress on the knees.
Understanding the various causes of knee pain is crucial for accurate diagnosis and effective treatment. If you’re experiencing persistent knee pain, it’s advisable to consult a healthcare practitioner to identify the underlying cause and receive appropriate guidance on managing and alleviating your symptoms.
Treatment Options
1. Rest and Ice
- Rest: Resting the affected knee is essential, especially during acute flare-ups or immediately after an injury. Avoiding activities that exacerbate pain allows the joint to heal and inflammation to subside.
- Ice: Applying ice to the knee for 15-20 minutes several times a day helps reduce swelling and numbs the area, providing pain relief. Be sure to wrap the ice pack in a cloth to prevent direct contact with the skin.
2. Physical Therapy
- Physical therapy involves a range of exercises designed to strengthen the muscles around the knee joint, improve flexibility, and enhance overall joint stability.
- A physical therapist will assess your condition and create a customised exercise plan that may include stretching, strengthening, and balance exercises to alleviate pain and prevent future issues.
3. Medications
- Over-the-Counter Pain Relievers: Non-prescription pain relievers like ibuprofen (Advil) or acetaminophen (Tylenol) can help manage pain and reduce inflammation. However, they should be used under medical guidance, especially for long-term use.
- Prescription Medications: If over-the-counter options aren’t sufficient, your healthcare practitioner may prescribe stronger pain medications or anti-inflammatory drugs.
4. Bracing and Support
- Knee braces provide stability and support to the joint, reducing strain and promoting proper alignment. Different types of braces are available, including sleeves for mild support and more rigid braces for post-injury recovery.
5. Injections
- Corticosteroid Injections: These injections deliver anti-inflammatory medication directly into the knee joint, providing rapid relief from pain and swelling. They are particularly effective for conditions like arthritis or bursitis.
- Hyaluronic Acid Injections: Hyaluronic acid injections may be recommended for individuals with knee osteoarthritis. These injections help lubricate the joint and reduce friction, easing pain and improving mobility.
6. Surgery
- Arthroscopy: Minimally invasive arthroscopic procedures can repair or remove damaged tissue in the knee, such as repairing torn ligaments or removing debris from the joint.
- Total Knee Replacement: In severe cases of osteoarthritis or irreparable joint damage, a total knee replacement surgery may be considered. This procedure involves replacing the damaged joint surfaces with artificial implants.
7. Lifestyle Changes
- Weight Management: Maintaining a healthy weight can significantly reduce stress on the knee joints, preventing or alleviating conditions like osteoarthritis.
- Low-Impact Activities: Engaging in low-impact exercises like swimming or cycling can help maintain joint health without placing excessive strain on the knees.
- Proper Body Mechanics: Learning and practising proper body mechanics during daily activities, such as bending and lifting, can prevent unnecessary stress on the knees.
Natural Remedies for Knee Pain
In addition to conventional medical treatments, several natural remedies and lifestyle adjustments can complement your efforts to manage and alleviate knee pain. It’s important to note that these remedies are generally suitable for mild cases of knee discomfort and should be discussed with a healthcare practitioner before implementation, especially if you have a preexisting medical condition or are taking medications. Here are some natural approaches to consider:
1. Cold and Heat Therapy
- Cold Packs: Applying a cold pack to the affected knee can help reduce inflammation and numb the area, providing temporary relief from pain. Use an ice pack wrapped in a cloth for around 15-20 minutes several times a day.
- Heat Therapy: Applying heat, such as a warm towel or heating pad, can help relax the muscles around the knee and improve blood circulation. Heat therapy can be especially beneficial before engaging in gentle exercises or stretches.
2. Gentle Knee Exercises and Stretches
- Engaging in low-impact exercises and gentle stretches can help maintain flexibility, improve joint mobility, and strengthen the muscles around the knee. Consult a physical therapist for guidance on appropriate exercises based on your condition.
3. Maintaining a Healthy Weight
- Carrying excess body weight stresses the knee joints, leading to increased wear and tear. Maintaining a healthy weight through a balanced diet and regular exercise can reduce the strain on your knees.
4. Anti-Inflammatory Foods
- Incorporating foods rich in anti-inflammatory properties into your diet can help manage knee pain. Omega-3 fatty acids found in fatty fish like salmon, walnuts, and flaxseeds, as well as spices like turmeric and ginger, have been shown to have potential anti-inflammatory effects.
5. Epsom Salt Baths
- Epsom salt contains magnesium sulphate, which is believed to have muscle-relaxing properties. Soaking your knees in a warm Epsom salt bath can provide relief from muscle tightness and discomfort.
6. Acupuncture
- Acupuncture involves the insertion of thin needles into specific points on the body to promote energy flow and alleviate pain. Some people report experiencing pain relief and improved mobility after acupuncture sessions.
7. Herbal Supplements
- Certain herbal supplements like devil’s claw, Boswellia, and white willow bark are traditionally believed to have anti-inflammatory and pain-relieving properties. However, it’s crucial to consult a healthcare practitioner before taking any herbal supplements, as they can interact with other medications or have side effects.
Remember that natural remedies might not be as potent as medical interventions for severe knee pain or conditions like fractures or advanced arthritis. It is essential to maintain open communication with your healthcare practitioner and seek their guidance before incorporating any natural remedies into your knee pain management plan.
A comprehensive approach that combines natural remedies, lifestyle adjustments, and medical treatments can provide the best results in alleviating knee discomfort and improving overall joint health.
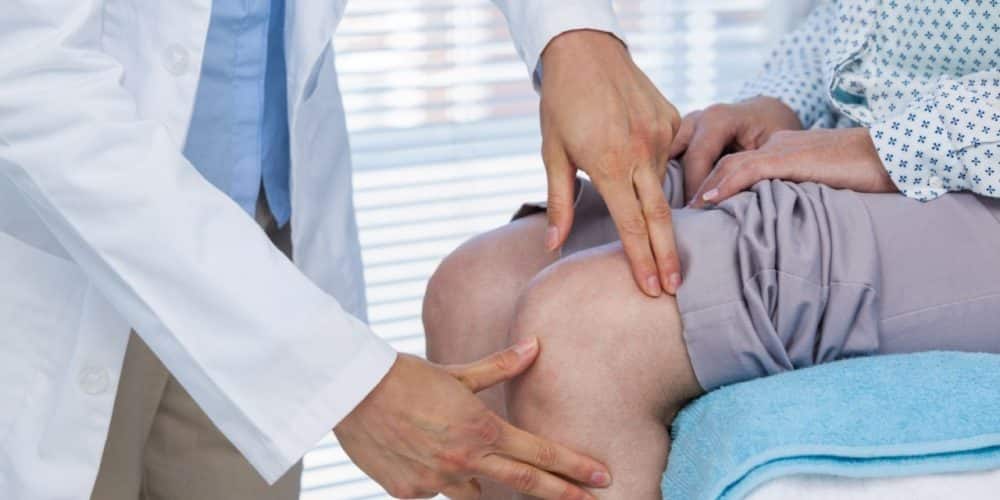
When to Seek Professional Help
Knowing when to seek professional medical assistance is crucial for effectively addressing knee pain and preventing potential complications. While home remedies and self-care strategies can offer relief for mild cases, certain signs and symptoms warrant a visit to a healthcare practitioner:
- Persistent or Worsening Pain: If your knee pain persists beyond a few days and shows no signs of improvement, or if it worsens over time despite rest and home treatments, it’s a clear signal that you should consult a healthcare practitioner. Prolonged pain might indicate an underlying issue that requires expert evaluation and intervention.
- Limited Range of Motion: Difficulty in fully extending or bending your knee can indicate a more serious problem, such as a ligament tear, cartilage damage, or arthritis. A healthcare practitioner can perform diagnostic tests to identify the cause and recommend appropriate treatment.
- Swelling and Inflammation: If your knee is swollen, tender, or warm to the touch, it could be a sign of inflammation or infection. Inflammation may result from various causes, such as injury, arthritis, or other medical conditions. However, if the swelling is accompanied by fever, redness, and increased pain, it’s crucial to seek medical attention promptly, as it might indicate an infection that requires immediate treatment.
- Unexplained Fever: The presence of a fever alongside knee pain should never be ignored. It might indicate an underlying infection, such as septic arthritis, which is a serious condition requiring swift medical intervention. Seek medical help immediately if you experience fever along with knee discomfort.
- Inability to Bear Weight: If you find it challenging or impossible to put weight on the affected knee, it could be indicative of a severe injury, such as a fracture, ligament tear, or dislocation. Avoid attempting to walk if you experience this symptom, and consult a healthcare practitioner as soon as possible.
- History of Chronic Conditions: If you have a history of conditions like osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis, or other chronic joint-related issues, it’s important to consult your healthcare practitioner, even for minor flare-ups, regularly. Managing these conditions properly can prevent further deterioration and enhance your overall joint health.
- Sudden Onset of Intense Pain: If you experience sudden, intense, and sharp pain in your knee without apparent cause, it’s advisable to seek immediate medical attention. Such pain could be a result of a serious injury that requires swift diagnosis and management.
- Changes in Mobility: If you notice a significant decline in your ability to move, walk, or perform everyday activities due to knee pain, it’s a clear indication that professional assessment is necessary. Ignoring these limitations could lead to further complications and hinder your quality of life.
In summary, understanding when to seek professional help is vital for accurately diagnosing the underlying cause of your knee pain and ensuring appropriate treatment. Early intervention can prevent complications, promote faster recovery, and help you regain optimal knee function.
If you need more clarification about whether to consult a healthcare practitioner, it’s always safer to err on the side of caution and schedule an appointment to address your concerns. Your health and well-being are worth the attention and care of healthcare practitioners who can guide you toward the most suitable treatment plan for your unique situation.
Conclusion
Knowledge truly is power in the journey to understanding and addressing knee pain. By recognising the various causes of knee pain, exploring treatment options, and knowing when to seek professional help, you’re equipped to take charge of your knee health and overall well-being. Remember that each individual’s experience with knee pain is unique, and what works for one person may not work for another. Finding the right combination of remedies and treatments often requires a bit of trial and error.
Now, it’s your turn to take action! Reflect on your experiences and any knee pain you might be dealing with. Have you identified the potential cause of your discomfort? Are you practising appropriate home remedies and self-care strategies? Are there any red flags that suggest it’s time to consult a healthcare practitioner? Your knee health matters, and taking proactive steps can lead to improved mobility, reduced pain, and a higher quality of life.
Have you ever tried any home remedies or treatments for knee pain, and if so, which ones have provided you with relief? Feel free to share your experiences and insights in the comments below. Remember, your journey toward managing knee pain can inspire and help others who might be facing similar challenges.
Content Summary
- No matter if you are an athlete, a fitness fanatic, or just someone who loves remaining active, it is crucial to have a solid awareness of the underlying issues that cause knee discomfort, as well as the variety of treatment options that are most likely to be successful.
- So, if you’re seeking insights to alleviate your discomfort, regain mobility, or simply enhance your knowledge about knee health, you’ve come to the right place.
- Knee pain is a frequent problem that may affect people of any age and be brought on by a wide range of various types of activity.
- Whether you are an athlete, a fitness enthusiast, or someone who follows a more sedentary lifestyle, experiencing soreness in the knees may significantly impact your quality of life.
- In order to attain effective management and long-term relief from knee pain, it is essential to get a grasp of the factors that contribute to the condition and the treatment choices currently accessible.
- In this article, we will investigate the multiple factors that may lead to knee discomfort, and we will also investigate the several therapy methods that might assist you in regaining mobility and comfort.
- Ligament tears, especially the anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) and medial collateral ligament (MCL) are prevalent among athletes and those involved in activities that involve sudden stops, changes in direction, or direct blows to the knee.
- Tears in the meniscus can result from twisting movements or direct trauma, leading to pain, swelling, and limited knee movement.
- Bursitis of the knee is characterised by localised pain, swelling, and tenderness in the vicinity of the afflicted bursa.
- Engaging in repetitive movements, especially without adequate rest and recovery, can strain the knee joint and its surrounding structures.
- Activities such as running, cycling, or kneeling can lead to overuse injuries, causing pain, inflammation, and discomfort in the knee area.
- Resting the affected knee is essential, especially during acute flare-ups or immediately after an injury.
- Applying ice to the knee for 15-20 minutes several times a day helps reduce swelling and numbs the area, providing pain relief.
- Physical therapy involves a range of exercises designed to strengthen the muscles around the knee joint, improve flexibility, and enhance overall joint stability.
- A physical therapist will assess your condition and create a customised exercise plan that may include stretching, strengthening, and balance exercises to alleviate pain and prevent future issues.
- If over-the-counter options aren’t sufficient, your healthcare practitioner may prescribe stronger pain medications or anti-inflammatory drugs.
- Knee braces provide stability and support to the joint, reducing strain and promoting proper alignment.
- These injections deliver anti-inflammatory medication directly into the knee joint, providing rapid relief from pain and swelling.
- Hyaluronic acid injections may be recommended for individuals with knee osteoarthritis.
- Minimally invasive arthroscopic procedures can repair or remove damaged tissue in the knee, such as repairing torn ligaments or removing debris from the joint.
- In addition to conventional medical treatments, several natural remedies and lifestyle adjustments can complement your efforts to manage and alleviate knee pain.
- Maintaining a healthy weight through a balanced diet and regular exercise can reduce the strain on your knees.
- Incorporating foods rich in anti-inflammatory properties into your diet can help manage knee pain.
- Soaking your knees in a warm Epsom salt bath can provide relief from muscle tightness and discomfort.
- Remember that natural remedies might not be as potent as medical interventions for severe knee pain or conditions like fractures or advanced arthritis.
- It is essential to maintain open communication with your healthcare practitioner and seek their guidance before incorporating any natural remedies into your knee pain management plan.
- A comprehensive approach that combines natural remedies, lifestyle adjustments, and medical treatments can provide the best results in alleviating knee discomfort and improving overall joint health.
- Knowing when to seek professional medical assistance is crucial for effectively addressing knee pain and preventing potential complications.
- If your knee pain persists beyond a few days and shows no signs of improvement, or if it worsens over time despite rest and home treatments, it’s a clear signal that you should consult a healthcare practitioner.
- The presence of a fever alongside knee pain should never be ignored.
- Seek medical help immediately if you experience fever along with knee discomfort.
- If you have a history of conditions like osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis, or other chronic joint-related issues, it’s important to consult your healthcare practitioner, even for minor flare-ups, regularly.
- If you experience sudden, intense, and sharp pain in your knee without apparent cause, it’s advisable to seek immediate medical attention.
- In summary, understanding when to seek professional help is vital for accurately diagnosing the underlying cause of your knee pain and ensuring appropriate treatment.
- If you need more clarification about whether to consult a healthcare practitioner, it’s always safer to err on the side of caution and schedule an appointment to address your concerns.
- Your health and well-being are worth the attention and care of healthcare practitioners who can guide you toward the most suitable treatment plan for your unique situation.
- Knowledge truly is power in the journey to understanding and addressing knee pain.
- By recognising the various causes of knee pain, exploring treatment options, and knowing when to seek professional help, you’re equipped to take charge of your knee health and overall well-being.
- Finding the right combination of remedies and treatments often requires a bit of trial and error.
- Your knee health matters, and taking proactive steps can lead to improved mobility, reduced pain, and a higher quality of life.
- Remember, your journey toward managing knee pain can inspire and help others who might be facing similar challenges.
FAQs
1. What are the common risk factors for developing knee pain?
Several factors can increase the risk of developing knee pain. Age, obesity, previous knee injuries, family history of joint problems, engaging in high-impact sports or activities, and having certain medical conditions like arthritis are some common risk factors.
2. How do I know when to see a healthcare practitioner for my knee pain?
If you experience persistent or worsening knee pain that interferes with your daily activities, it’s advisable to consult a healthcare practitioner. Seek medical attention if you cannot bear weight on the knee, notice swelling or redness, or if the pain is accompanied by fever or warmth around the joint.
3. Can exercise worsen knee pain?
While proper exercise is generally beneficial for knee health, improper form, overexertion, or engaging in high-impact activities without appropriate conditioning can exacerbate knee pain. Working with a healthcare practitioner or physical therapist is important to design an exercise routine that supports knee health without causing harm.
4. Are there any natural remedies for knee pain relief?
Some natural remedies may offer relief for mild knee pain. Applying cold or hot packs, gentle knee stretches and exercises, maintaining a healthy weight, and consuming anti-inflammatory foods like fatty fish, turmeric, and ginger can contribute to reducing discomfort. However, consult a healthcare practitioner before relying solely on natural remedies.
5. Can knee pain be prevented?
While preventing knee pain entirely is impossible, certain lifestyle choices can minimise the risk. Maintaining a healthy weight, wearing appropriate footwear, practising proper body mechanics, staying active with low-impact exercises, and avoiding sudden increases in intensity during physical activities can help reduce the likelihood of knee pain.